Multi-channel algebraic scattering (MCAS)
The Multi-Channel Algebraic Scattering (MCAS) method is a novel approach for solving coupled-channel scattering equations to, in principle, analyse any discrete-body quantum scattering problem. It does this in an algebraic fashion, and when used for nuclear scattering problems it takes proper consideration of the Pauli principle, whatever model may be used to define the coupled-channel interaction potentials of the two scattering bodies. This is achieved by separable expansions of these potentials into a finite set of optimal form factors called sturmians.
Applications to date have analysed low-energy nucleon-nucleus and nucleon-\(\alpha\) scattering data for cases in which the nuclear target is of low mass number. The method is capable of modelling situations where target states themselves are allowed to be particle emitting resonances, which is important in analysing results from recent experimental studies using radioactive ion beams.
As the interaction potentials used may be phenomenological, an optimised search of the parameter space is desirable.
Selected bibliography
K. Amos, L. Canton, G. Pisent, J. P. Svenne, and D. van der Knijff, Nucl. Phys. A728 65, (2003).
Detailed description of the MCAS method, including the sturmian expansion method, implementation of the Pauli principle by orthogonalising pseudo-potentials, development of collective interaction potentials of rotor character, and application to the system \(n+^{12}\text{C}\).L. Canton, G. Pisent, J. P. Svenne, D. van der Knijff, K. Amos, and S. Karataglidis Phys. Rev. Lett. 94, 122503 (2005).
Further details of the implementation of the Pauli principle.L. Canton, G. Pisent, J. P. Svenne, K. Amos, and S. Karataglidis, Phys. Rev. Lett. 96, 072502 (2006)
Prediction of narrow resonance states in the system \(p+^{14}\text{O}\), representing predicted states of \(^{15}\text{F}\) later verified experimentally (see Figure 1).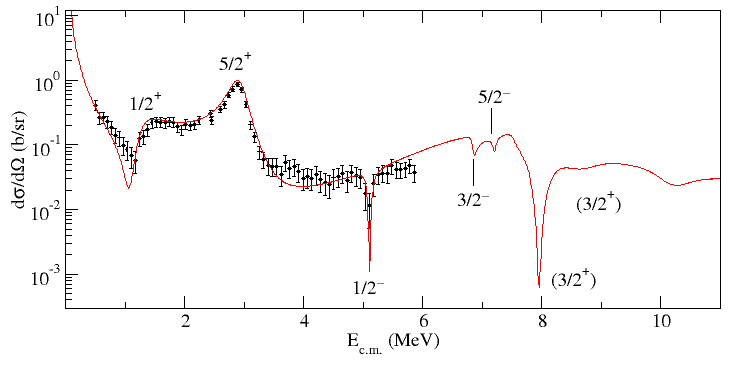
Figure 1 \(180^\circ\) \(p+^{14}\text{O}\) elastic scattering cross section. MCAS result (red) with data from F. de Grancey et al., Phys. Lett. B758, 26 (2016).
P. R. Fraser, K. Massen-Hane, K. Amos, I. Bray, L. Canton, R. Fossión, A. S. Kadyrov, S. Karataglidis, J. P. Svenne, and D. van der Knijff Phys. Rev. C94, 034603.
Extension of the method to incorporate particle-unstable target states for applications to RIB.J. P. Svenne, L. Canton, K. Amos, P. R. Fraser, S. Karataglidis, G. Pisent, and D. van der Knijff, Phys. Rev. C95, 034305.
Development of collective interaction potentials of vibrator character, and application to the system \(n+^{16}\text{O}\).